The Goods and Services Tax (GST), implemented on July 1, 2017, is one of India’s most significant tax reforms, replacing multiple indirect taxes like VAT, service tax, and excise duty. Based on the principle of “One Nation, One Tax,” GST brings uniformity and transparency across states. Any business exceeding the prescribed turnover threshold is legally required to register under GST. Upon registration, a unique 15-digit GSTIN (GST Identification Number) is issued, enabling businesses to collect GST, claim input tax credits, and ensure compliance with Indian tax laws. GST registration not only ensures legal compliance but also enhances business credibility, allows access to wider markets (including e-commerce), and simplifies tax filing and interstate trade.
Everything you need to know about GST registration will be covered in this article, including its definition, eligibility requirements, necessary paperwork, the detailed registration procedure, and the exemption categories. Whether you are a compliance specialist, a startup founder, or an established business owner, this thorough guide will help you comprehend how GST registration operates and how it can be handled successfully with expert assistance.
What is GST registration?
The formal procedure for registering a company or individual under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India is called GST Registration. Following registration, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) assigns a unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN). Businesses that achieve specific revenue requirements or fit into particular categories outlined in the GST Act are required to have this 15-digit PAN-based, state-specific number.
Simply said, companies are required by law to register for GST in order to: Get GST from clients When making purchases, claim the Input Tax Credit (ITC). Submit GST returns. Engage in formal trade, e-commerce, and tenders. It is necessary to guarantee tax adherence and prevent fines under the GST regulations. A firm cannot legitimately collect taxes from clients or pass on the tax credit on goods or services it provides if it is not registered for GST.
For instance, you must register for GST if your company generates more than Rs.40 lakhs in revenue (Rs.20 lakhs for commodities in special category states). Similar to this, GST registration is required even if you don't surpass the threshold if you sell on an online marketplace like Amazon or Flipkart.
Who needs GST registration?
Certain types of people and enterprises must register for GST in accordance with the Goods and Services Tax statute. These consist of:
-
Interstate suppliers,
-
E-commerce operators, and import-export businesses, is described in the section that follows.
-
Individuals who are taxable on a casual basis
-
Casual taxable persons who are not residents.
-
Those who make any taxable interstate shipments representatives of a registered taxpayer.
-
Owners of online stores.
-
TDS/TCS deductor, individuals who operate in a state other than their home state.
-
Individuals who sell goods on online marketplaces like Amazon and Flipkart.
-
people employed in the import-export sector.
-
Individuals who are liable for reverse charge taxes.
-
companies that were formerly subject to taxes including service tax, VAT, and excise taxes.
-
People in charge of an aggregator business.
-
Distributors of Input Services.
-
Indian service providers of OIDAR (Online Information Database Access and Retrieval).
Who is Liable to Register Under GST in India?
The yearly turnover, business type, and geographic location of an organization are the main factors that determine its eligibility for GST registration. The primary requirements for determining whether a business must register for GST are listed below.
Turnover Thresholds for GST Registration
In India GST registration is compulsory for businesses once they cross the specified turnover threshold, as defined under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law. These threshold limits for GST registration differ based on the type of supply (goods or services) and the geographical location of the business, especially in special category states.
- GST Turnover Limit for Goods Suppliers Businesses engaged in the supply of goods are required to register under GST if their annual aggregate turnover exceeds: Rs.40 lakhs in most Indian states Rs.20 lakhs in special category states, such as Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, and others.
- GST Turnover Limit for Service Providers Service providers offering services like consulting, legal, IT, hospitality, and freelancing are required to register under GST if their total turnover exceeds: Rs.20 lakhs in regular states Rs.10 lakhs in special category states
Special Scenarios Where GST Registration
It is Mandatory (Irrespective of Turnover) Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, there are specific cases where GST registration is mandatory even if the business’s annual turnover is below the standard threshold-
-
Businesses Involved in Interstate Transactions: Any person or business engaged in the interstate supply of goods or services i.e., supplying across state borders must obtain GST registration regardless of their turnover. This rule is applicable to manufacturers, traders, consultants, freelancers, and others operating across states.
-
Occasional Suppliers Without Fixed Place of Business: They are also known as a casual taxable person is someone who occasionally supplies goods or services in a different state where they don’t have a fixed place of business.
-
Foreign Entities Making Taxable Supplies in India: If an individual or entity that is not a resident of India supplies taxable goods or services in the country, they are classified as a non-resident taxable person (NRTP). In such cases, GST registration is compulsory, and registration must be obtained at least five days prior to the commencement of business.
-
Centralized Units Distributing Input Tax Credit: They are also known as An Input Service Distributor is a business that receives input services centrally and distributes the input tax credit (ITC) to different branches or units.
Voluntary GST Registration
When some Businesses opt in even below the Threshold Businesses that do not meet the mandatory GST turnover threshold may still opt for voluntary GST registration. While it is not legally required for entities with lower turnover, many businesses choose to register under GST to avail themselves of various operational and strategic benefits. Below are the key reasons why opting for voluntary GST registration in India can be advantageous:
-
Claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on Business Expenses Voluntarily registered businesses are eligible to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on the GST paid for purchases made in the course of business. This includes goods, raw materials, and services used for business operations.
-
Enhance Business Credibility and Trust Having a GSTIN (GST Identification Number) increases the credibility of your business in the eyes of vendors, customers, and government agencies. It signals that the business is tax-compliant, transparent, and professionally managed, which is especially important when dealing with B2B clients, corporates, or large institutions. It enables listing products on e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, and others, which mandate GST registration for sellers.
GST Registration Exemptions
In India Not every business is obligated to register under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. Several GST registration exemptions are available for certain categories of businesses, goods, and services. These exemptions under GST typically apply to:
-
Agricultural Activities and Produce GST registration is not required for agriculturists engaged in the supply of agricultural produce resulting from cultivation. Farming activities and unprocessed food products are generally exempt from GST, unless they fall under taxable categories.
-
Small Businesses Below GST Turnover Limit Small enterprises whose annual turnover is below the prescribed GST threshold (Rs.40 lakhs/Rs.20 lakhs/Rs.10 lakhs, depending on business type and state) are exempt from compulsory registration—unless they engage in inter-state supply, e-commerce, or other specified taxable activities.
-
Supply of GST-Exempt Goods and Services Businesses dealing exclusively in exempt goods or services such as alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum products, healthcare services, and certain transport services are not required to obtain GST registration.
Documents Required for GST Registration in India
-
PAN and Aadhaar of the Applicant A valid Permanent Account Number (PAN) is mandatory for GST registration. The Aadhaar card of the applicant is required for authentication through Aadhaar-based e-verification.
-
Certificate of Incorporation or Business Registration Proof, Proof of incorporation for companies, LLPs, or registered partnerships must be submitted. This includes business registration documents issued by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), partnership deeds, or other legal certificates.
-
Identity, Address Proof & Photographs of Promoters/Partners/Directors Self-attested copies of PAN, Aadhaar, Voter ID, or Passport of promoters/director/ partners. Recent passport-size photographs of all authorized persons.
-
Proof of Principal Place of Business Address proof such as electricity bill, property tax receipt, rent agreement, or NOC from the owner.
-
Bank Account Proof Submit the first page of a bank passbook, cancelled cheque, or recent bank statement in the name of the business.
-
Authorization Letter or Board Resolution A Letter of Authorization (for proprietorship/partnership) or Board Resolution (for companies) appointing the Authorized Signatory. The Authorized Signatory must have a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) if registering a company or LLP.
Step-by-Step Process for GST Registration in India
Step 1. Visit the GST Portal at https://services.gst.gov.in/services/quicklinks/registration
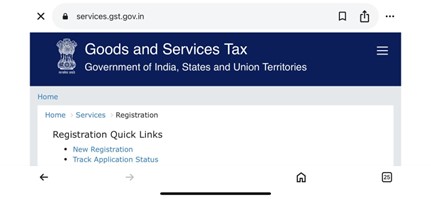
Step 2. Click on New Registration
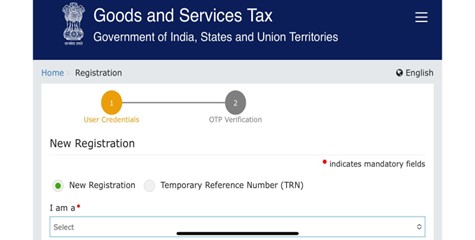
Step 3. After clicking on New Registration a Form will Open like this you have to enter details
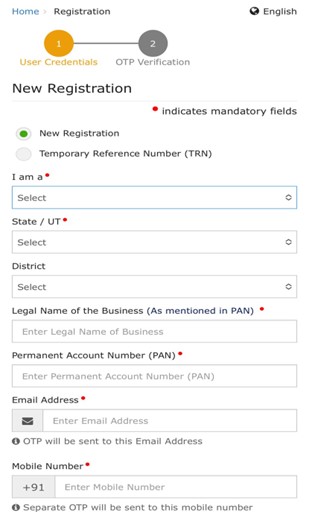
Step 4. After filling in all the required details, you will receive two separate OTP’s one on phone number and other on E-mail address for verification.
Step 5. Upon successful OTP verification, a Temporary Reference Number (TRN) will be generated. This TRN will also be sent to your registered mobile number and email address make sure to note it down for future use.
Step 6. Go back to the GST registration page and select the “Temporary Reference Number (TRN) option.
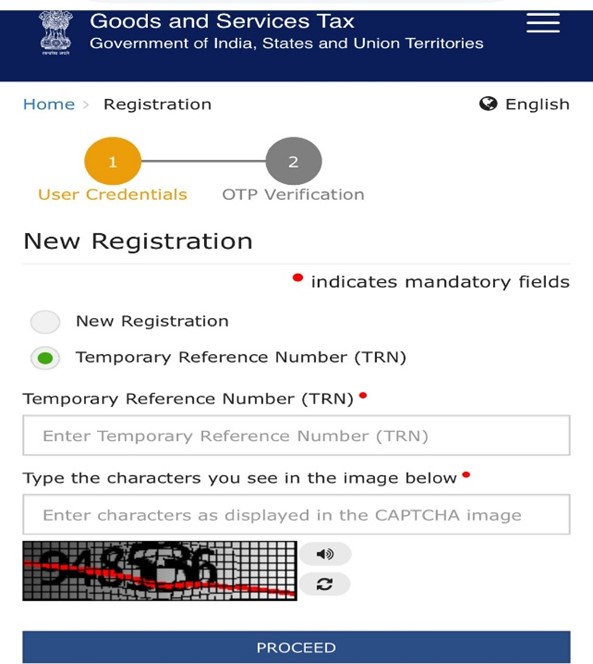
Step 7. Enter your TRN, fill in the captcha code, and click on proceed.
Step 8. You will receive another OTP on your registered mobile/email for verification enter OTP and proceed.
Step 9. Once verified you will be redirected to your GST registration dashboard where your application will be saved as a “draft”.
Step 10. Click on the edit icon next to the draft application to begin filling out the complete GST registration form.
How to track GST registration application?
Step 1 . Visit website https://services.gst.gov.in/services/arnstatus
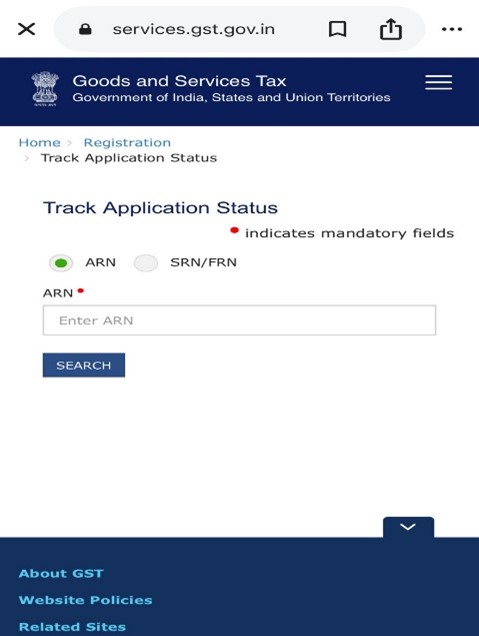
Step 2. You will see two options to track the status:
-
ARN (application reference number)
-
SRN (Service request number) for MCA (for companies)
Step 3. Enter the ARN you received after submitting the GST application.
Step 4. Enter the captcha code displayed on the screen.
Step 5. Click on the search button.
What is the GSTIN?
Every taxpayer who registers under the GST system in India is given a unique 15-digit alphanumeric identifier known as the Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN). After completing the GST registration process on the GST portal, it is issued by the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN).
GSTIN Structure- According to the Indian Census, the first two digits (for example, 09 for Uttar Pradesh and 27 for Maharashtra) represent the state code. The next ten numbers are the Permanent Account Number (PAN) of the taxpayer. The thirteenth digit shows how many registrations the taxpayer has in a certain state. The default 14th digit is Z. The 15th digit is a validity check code.
GSTIN example: 27ABCDE1234F1Z5.
Time Frame for GST Registration
Applications for GST registration must be submitted within 30 days of becoming eligible for GST registration. When the entity reaches the threshold aggregate turnover, starts an interstate supply business, or engages in e-commerce, the individual must register for GST.
Penalties for Not Registering Under GST in India
A penalty of 10% of the tax amount owed, up to a minimum of Rs. 10,000, must be paid by the offender who fails to pay taxes or makes short payments (real errors).
If the offender will fully avoided paying taxes, the penalty will be 100% of the tax amount owed.
Our Support for GST Registration
We make the entire GST registration process easier for you at Compliance Calendar LLP. Whether you are a freelancer, MSME, startup, e-commerce merchant, or expanding business, our knowledgeable staff guarantees a speedy, error-free registration process. What We Provide:
-
Complete help with submitting a GST application via the GST portal Assist with the preparation and verification of documents
-
Support for e-KYC authentication based on Aadhaar for quicker clearance
-
Application progress tracking in real time
-
Timely handling of GST officer inquiries and notifications Help with setting up compliance and acquiring a GSTIN certificate
Our experts, who have thousands of successful files under their belts and years of expertise, make sure you're GST-compliant right away so you can concentrate on expanding your company.
Start now! For a brief consultation, send us an email at info@ccoffice.in or message us on WhatsApp on 9988424211
 FAQ’s
FAQ’s
Q1. Can I cancel my GST registration?
Ans. Yes, if your business is no longer liable under GST or is closed, you can file an application for cancellation through the GST portal
Q2. Can I voluntarily register under GST even if my turnover is below the threshold?
Ans. Yes, voluntary registration is allowed. It offers benefits such as input tax credit, better business credibility, and access to interstate and online markets.
Q3. What happens if I don’t register under GST?
Ans. If you are liable but fail to register, a penalty of Rs.10,000 or the amount of tax evaded (whichever is higher) may be levied under Section 122 of the CGST Act
Q4. Is GST registration free of cost?
Ans. Yes, registering on the official GST portal is free. However, professional assistance may involve service charges for document preparation and filing.
Q5. How long does GST registration take?
Ans. If Aadhaar authentication is used, GST registration is usually approved within 1–7 working days. Without it or if clarification is required, approval may take up to 30 days.
Q6. What are the documents required for GST registration?
Ans. Key documents include PAN, Aadhaar, business address proof, bank account details, photos, and authorization letter or board resolution for the authorized signatory.
Q7. What is the GSTIN and how do I get it?
Ans. GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) is a 15-digit unique ID issued upon successful registration. You receive it after applying on the GST portal (gst.gov.in) and completing document verification.











_crop10_thumb.jpg)





_crop10_thumb.jpg)




























-Form_crop10_thumb.jpg)

_crop10_thumb.jpg)























_learn_crop10_thumb.jpeg)
































_crop10_thumb.jpg)

_crop10_thumb.jpg)





















_crop10_thumb.jpg)















_for_Foreign_Directors_learn_crop10_thumb.jpeg)




_Act,_2015_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)



































_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)