Business compliance refers to the set of legal and regulatory obligations that every business entity must follow to operate lawfully in India. These obligations differ based on factors such as the form of the entity, the nature of its activities, the number of employees, turnover levels, and the industry in which it operates. From corporate filings and tax returns to labour laws and sector-specific licences, compliance ensures that a business functions within the framework prescribed by law.
Compliance is not a one-time activity completed at the time of incorporation; it is an ongoing responsibility that continues throughout the life of the business. Regular adherence to compliance requirements promotes transparency, strengthens governance, and builds credibility with regulators, investors, and stakeholders. Ignoring or delaying compliance can result in financial penalties, legal proceedings, cancellation of registrations, and long-term reputational damage, which can severely impact business growth and continuity.
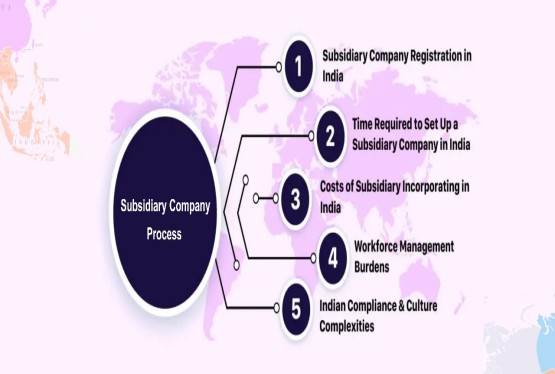
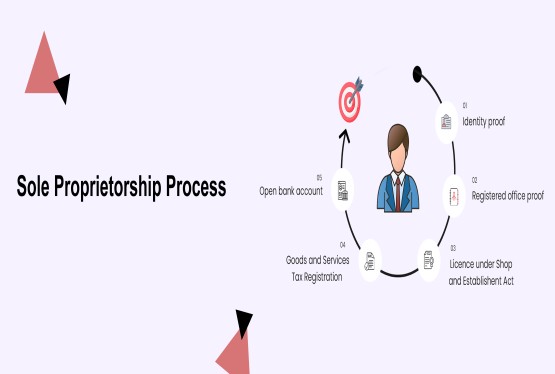
Entity Formation and Structural Compliances
Entity formation and structural compliances are the foundation of any legally compliant business. These compliances establish the legal identity, ownership structure, and governance framework of an entity. They ensure that the business is properly recognised under law and operates with transparency, accountability, and documented decision-making.
Companies
Companies are governed by a detailed statutory framework and are subject to regular governance and reporting obligations. They are required to conduct board meetings and shareholder meetings within prescribed timelines to ensure collective decision-making and oversight. Companies must also maintain statutory registers and minutes, which serve as official records of directors, shareholders, and key decisions. In addition, companies must file annual and event-based statutory forms to report financials and changes such as appointment of directors, changes in capital, or registered office. Audit and disclosure requirements further ensure financial transparency and protect stakeholder interests.
LLPs and Partnerships
LLPs and partnerships enjoy comparatively simpler compliance requirements but are still subject to periodic legal obligations. They must file annual statements and returns, keep updated records of partners and agreements, and comply with audit requirements once prescribed thresholds are crossed. These compliances ensure financial discipline and clarity in partner responsibilities.
Corporate Governance and Statutory Reporting
Corporate governance and statutory reporting compliances ensure that a business operates in a transparent, accountable, and well-documented manner. These compliances require businesses to follow proper approval processes, maintain records of decisions, and report significant changes to regulatory authorities. Strong governance practices build stakeholder confidence and reduce the risk of disputes or regulatory action.
Regular Governance Obligations
Businesses are required to obtain board approvals for key managerial and financial decisions to ensure collective responsibility and oversight. Certain important matters also require shareholder approval, which protects the interests of owners and investors. Additionally, the maintenance of resolutions, minutes, and statutory records is mandatory, as these documents provide legal evidence of compliance and decision-making.
Event-Based Compliances
Whenever a business undergoes significant changes such as a change in directors or partners, shift of registered office, capital infusion or restructuring, or creation of loans, charges, or related party transactions specific filings and disclosures must be made within prescribed timelines. Failure to comply with these event-based requirements often leads to complications during audits, funding rounds, mergers, or due diligence exercises.
Income Tax and Direct Tax Compliances
Income tax and direct tax compliances are mandatory for all business entities, irrespective of their size or form. These compliances ensure that income is properly reported, taxes are paid on time, and financial records are maintained accurately in accordance with law.
Annual Tax Obligations
Every business is required to file its income tax return within the prescribed due date, declaring its income, expenses, and tax liability. Where applicable, businesses must also pay advance tax in instalments during the financial year to avoid interest liability. In addition, proper books of accounts must be maintained, as they form the basis for tax computation, audits, and assessments.
TDS and Reporting
Businesses making specified payments must deduct and deposit tax at source (TDS) within prescribed timelines. They are also required to file periodic TDS returns and issue TDS certificates to deductees. Any error or delay in these compliances can lead to interest, penalties, and disallowance of related expenses.
GST and Indirect Tax Compliances
GST and indirect tax compliances are highly technology-driven and require accurate documentation and regular reconciliation. Businesses must ensure that every transaction is properly recorded and reported on the GST portal, as mismatches or delays can easily trigger notices and audits.
Core GST Requirements
Businesses must obtain GST registration and ensure timely updates for any changes. They are required to issue tax-compliant invoices containing all mandatory details and file periodic GST returns along with payment of tax within prescribed timelines. These steps ensure proper reporting of outward and inward supplies.
Operational Controls
Effective GST compliance also involves reconciling input tax credit with vendor data, following e-invoicing and e-way bill rules where applicable, and monitoring vendor compliance. Failure to comply can result in blocking of input tax credit, penalties, and serious cash flow disruptions.
Labour Law and Employment Compliances
Once a business employs people, labour law and employment compliances become compulsory. These compliances are designed to protect employee welfare, ensure fair working conditions, and maintain harmony between employers and workers. Non-compliance can result in penalties, employee disputes, and legal action.
Employee Welfare Laws
Employers are required to register and make timely contributions under EPF and ESIC, where applicable, to provide social security benefits to employees. Professional tax compliance must be followed as per state laws, and Labour Welfare Fund contributions must be paid in applicable states. These laws ensure financial and social protection for employees.
Employment Documentation
Proper appointment letters and wage structures must be issued to define terms of employment. Employers must maintain accurate attendance and payroll records and comply with statutory benefits such as bonus, gratuity, and leave entitlements. Proper labour compliance helps reduce workplace disputes and ensures legal protection for both employers and employees.
Workplace Safety and POSH Compliance
Workplace safety and employee dignity have become essential elements of modern business compliance. Laws relating to prevention of sexual harassment at the workplace require employers to create a safe, respectful, and inclusive working environment. POSH compliance is not limited to policy adoption; it reflects an organisation’s commitment to ethical governance and employee well-being.
POSH Obligations
Eligible establishments must constitute an Internal Committee in the prescribed manner to address complaints of sexual harassment. They are required to adopt and implement a POSH policy and ensure regular awareness and training programs for employees. These measures help prevent misconduct and provide a structured grievance redressal mechanism.
Governance Importance
Failure to comply with POSH requirements can lead to statutory penalties, serious reputational harm, and breakdown of governance standards. POSH compliance is often reviewed during audits, funding, and due diligence processes.
Data Protection and Digital Compliance
With businesses increasingly relying on digital platforms and technology, data protection and digital compliance have become critical legal responsibilities. Organisations routinely collect and process personal data of customers, employees, and vendors, making it essential to handle such data responsibly and in accordance with applicable laws. Proper data governance helps prevent misuse of information and protects business credibility.
Personal Data Handling
Businesses must ensure the lawful collection and use of personal data for legitimate purposes only. This includes following proper consent practices, issuing clear privacy notices, and ensuring transparency in how data is used. Additionally, organisations must implement secure storage and controlled access systems to prevent unauthorised use or leakage of sensitive information.
Cybersecurity Measures
Strong cybersecurity practices are equally important. Businesses should maintain a data breach response mechanism, enter into data protection agreements with vendors, and implement internal IT security controls such as access restrictions and system monitoring. Failure to comply with data protection norms can lead to regulatory action, financial loss, and erosion of customer trust.
Sector-Specific and Product-Based Compliances
Apart from general legal compliances, many businesses are required to obtain sector-specific and product-based approvals depending on the nature of their operations. These compliances are operational in nature and directly impact a business’s ability to manufacture, sell, or distribute goods and services legally.
Industry-Specific Approvals
Businesses operating in regulated sectors must obtain necessary licences such as food safety licences for food-related activities, manufacturing or factory licences for production units, and import-export registration for cross-border trade. These approvals ensure that businesses meet prescribed safety, quality, and regulatory standards.
Product and Quality Compliance
Certain products are subject to Legal Metrology requirements, mandatory quality and safety certifications, and environmental permissions. These compliances help protect consumers, ensure accurate measurements, and prevent environmental harm. Without these approvals, business operations may be restricted or declared unlawful.
Financial and Regulatory Compliances
Businesses operating in regulated sectors, especially in financial and capital market–related activities, are subject to enhanced regulatory scrutiny. Such entities must follow strict compliance frameworks to protect investors, maintain market integrity, and ensure fair conduct. Regulatory authorities closely monitor these businesses due to the sensitive nature of financial services.
Financial Services
Entities engaged in financial services must comply with registration and periodic reporting requirements prescribed by regulators. They are also required to maintain proper client disclosures and an effective grievance redressal mechanism to address complaints promptly. Adherence to conduct and ethical standards is critical to prevent conflicts of interest, mis-selling, and unfair practices.
Advisory and Digital Finance
Businesses offering advisory or digital finance services, even indirectly, must structure their activities carefully. Improper positioning or unregistered advisory services can lead to regulatory violations, penalties, or enforcement action, making compliance planning essential.
Contractual and Commercial Compliances
Legal compliance is not limited to statutory filings and registrations; it also extends to how a business manages its contracts and internal decision-making processes. Strong contractual and commercial compliances help define rights, obligations, and risk allocation, thereby reducing disputes and financial exposure.
Contract Management
Businesses must ensure that all agreements are properly drafted and legally enforceable, clearly outlining terms, responsibilities, and liabilities. Compliance with stamp duty and execution requirements is essential to make contracts legally valid and admissible in law. In addition, well-documented vendor and employee agreements help avoid misunderstandings, protect confidential information, and ensure continuity of operations.
Internal Governance
Effective internal governance requires a clear authority matrix and approval system to control decision-making and financial commitments. Maintaining proper records and audit trails of approvals, contracts, and transactions ensures transparency and accountability. Weak contractual compliance often results in disputes, revenue leakage, and legal losses.
Intellectual Property and Advertising Compliances
Protecting a business’s brand identity and ensuring responsible communication are important aspects of legal compliance. Intellectual property and advertising compliances help safeguard a company’s creative assets, prevent misuse by competitors, and ensure that customers are not misled by promotional activities.
Intellectual Property
Businesses should secure trademark and copyright protection to protect their brand names, logos, content, and creative works. Regular monitoring and enforcement of intellectual property rights helps prevent infringement, dilution of brand value, and potential legal disputes. Proactive IP protection strengthens market position and long-term business value.
Advertising Standards
Advertising and marketing communications must avoid misleading or false claims and comply with applicable consumer protection laws. Businesses are expected to present accurate information about their products and services, as non-compliant advertising can attract regulatory action, penalties, and loss of consumer trust.
Recent Compliance Trends and Regulatory Focus
Regulatory authorities have significantly strengthened their compliance and enforcement mechanisms by adopting technology-driven systems, data analytics, and inter-departmental information sharing. This shift has reduced manual intervention and increased the accuracy and speed of regulatory scrutiny across various laws.
With automated scrutiny and system-generated notices, even small discrepancies in filings or delays in compliance are quickly identified. Regulators now show reduced tolerance for non-compliance, and penalties are imposed more swiftly and consistently. There is also a growing focus on corporate governance, transparency, and data protection, reflecting higher expectations from businesses. In this evolving regulatory environment, businesses must regularly review and update their compliance frameworks to stay aligned with current laws, notifications, and enforcement practices.
Conclusion
Business compliance means following all the legal and regulatory rules required to run a business properly. It is not limited to filing forms or meeting deadlines, but involves maintaining clear processes, accurate records, and responsible management practices. When compliance is integrated into daily operations, businesses can avoid confusion, errors, and unnecessary legal issues.
A strong compliance framework helps businesses operate smoothly and builds confidence among investors, lenders, and authorities. Organisations that follow compliance requirements consistently face fewer disruptions, reduce the risk of penalties or legal action, and maintain a positive reputation. Rather than being a burden, compliance acts as a support system that enables steady growth, operational stability, and long-term business sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are business compliances?
Ans. Business compliances are the legal and regulatory obligations that an entity must follow to operate lawfully. These include corporate filings, tax compliances, labour laws, sector-specific licences, and governance requirements prescribed by law.
Q2. Do all businesses need to follow the same compliances?
Ans. No. Compliance requirements vary based on the type of entity, nature of business, turnover, number of employees, and industry sector. A small proprietorship and a large company do not have identical compliance obligations.
Q3. What are the most common compliances applicable to businesses?
Ans. Common compliances include company or LLP filings, income tax returns, GST returns, TDS compliance, labour law registrations, employment documentation, sector-specific licences, and record maintenance.
Q4. What happens if a business fails to comply with legal requirements?
Ans. Non-compliance can result in penalties, interest, legal notices, inspections, cancellation of registrations, and reputational damage. In serious cases, it may also affect funding, audits, and business continuity.
Q5. Are compliances a one-time requirement after registration?
Ans. No. Most compliances are ongoing and periodic, such as annual filings, monthly or quarterly tax returns, and event-based filings whenever there is a change in structure, management, or operations.
Q6. Why are labour law compliances important for employers?
Ans. Labour compliances protect employee rights and help employers avoid disputes, inspections, and penalties. Proper compliance ensures fair wages, social security benefits, and a legally compliant workplace environment.
Q7. How do sector-specific compliances affect businesses?
Ans. Sector-specific compliances determine whether a business can legally operate. Without required licences or approvals, businesses may face restrictions on manufacturing, selling, importing, or providing services.
Q8. Can compliance improve business credibility?
Ans. Yes. A strong compliance record builds trust with investors, banks, customers, and regulators. It also makes audits, due diligence, and expansion activities smoother and more reliable.
Q9. How often should businesses review their compliance requirements?
Ans. Businesses should review their compliance framework at least once a year or whenever there is a change in law, business structure, turnover, employee strength, or nature of operations.
Q10. Can professional support help in managing compliances?
Ans. Yes. Professional compliance support helps businesses track deadlines, interpret legal changes, prepare documentation accurately, and avoid penalties, making compliance management more efficient and reliable.












_crop10_thumb.jpg)





_crop10_thumb.jpg)




























-Form_crop10_thumb.jpg)

_crop10_thumb.jpg)























_learn_crop10_thumb.jpeg)
































_crop10_thumb.jpg)

_crop10_thumb.jpg)





















_crop10_thumb.jpg)















_for_Foreign_Directors_learn_crop10_thumb.jpeg)




_Act,_2015_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)



































_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)