Setting up a private limited company in India has become significantly simpler with reforms introduced under the Ease of Doing Business initiative of the MCA and the move has reduced procedural hurdles, saving time and effort for entrepreneurs. Yet, if the director happens to be a national from a country sharing a land border with India like China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, and Afghanistan., there are special security clearance requirements under the Companies Act, 2013 read with Companies (Appointment and Qualification of Directors) Amendment Rules, 2022, specially around the DIN allotment process, are important and major process for cross-border investors to understand before commencing operations.
DIN Requirement under Under Section 153 of the Companies Act, 2013
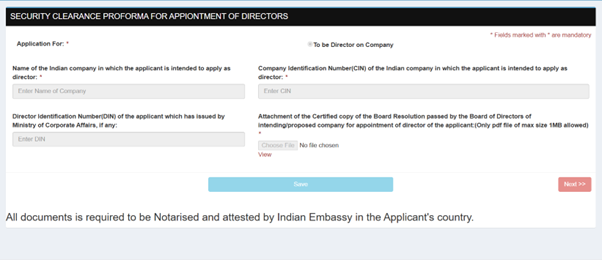
Every individual intending to be appointed as a director must apply for a DIN to the Central Government in Form DIR-3, accompanied by a prescribed fee of Rs.500 along with all supporting documents.
As per Rule 9 of the Companies (Appointment and Qualification of Directors) Rules, 2014:
-
Rule 9(1): An applicant for appointment as a director in an existing company must file Form DIR-3 electronically with the MCA.
-
Rule 9(3)(a)(iiia): A board resolution proposing the appointment is mandatory when joining an existing company.
-
Rule 9(3)(b): The form must be signed with the applicant’s Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and verified by a full-time company secretary, managing director, director, CEO, or CFO of the company.
Amendment for Nationals of Border-Sharing Countries
With effect from 1 June 2022, MCA introduced significant changes via the Companies (Appointment and Qualification of Directors) Amendment Rules, 2022, which mandate DIN security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) for individuals who are nationals of countries sharing a land border with India such as China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
The Amendment Inserts Two Key Provisions:
Rule 8 – Consent to Act as Director (Form DIR-2)
If the applicant is a national of a border-sharing country, MHA security clearance must be attached along with the consent form.
The declaration section now includes:
-
“I am not required to obtain security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs…” OR
-
“I am required to obtain security clearance…and the same has been obtained and attached.”
Rule 10 – DIN Application (Form DIR-3)
- No DIN application number will be generated unless the MHA security clearance is attached for nationals of border-sharing countries.
Countries Sharing Land Borders with India
The amendment applies to nationals of the following countries: China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
From 1 June 2022 onwards:
-
No DIN will be issued to nationals of the above-listed countries without MHA security clearance.
-
Chinese nationals, or nationals from other specified countries, must secure MHA approval before being appointed as directors in Indian companies.
FEMA Provisions on Investments from Border-Sharing Countries
Even before this MCA amendment, similar restrictions existed under FEMA regulations. As per the FDI policy:
-
Investments from entities or beneficial owners based in border-sharing countries can only be made through the Government approval route.
-
For Pakistan-based citizens/entities, investment is permitted only under the Government route and is prohibited in sectors like defence, space, atomic energy, and other restricted sectors.
Document & Information Requirements
When appointing a foreign resident individual as a director in an Indian company, particularly where DIN Security Clearance is required (including cases involving nationals from land-border sharing countries), certain documents and details must be submitted in the prescribed manner.
Below is a complete list of requirements for initiating the process:
Details and Documents of the Proposed Appointee
KYC and Identity Proofs
-
Present Address Proof: Latest Utility Bill or Bank Statement (self-attested), not older than 2 months.
-
Permanent Address / Correspondence Address Proof: Any one of the following – Voter ID, Aadhaar Card, or Driving License.
-
Citizenship ID Card – duly authenticated and notarised.
-
Nationality Proof – documentary evidence establishing nationality.
-
PAN Card (if issued in India).
-
Copy of Passport along with Visa Copy.
Personal and Professional Information
-
Professional details – current occupation, employer/organization name and address.
-
Place of birth and educational qualification.
-
Email ID and contact number.
-
Recent passport-size colour photograph.
Additional Declarations
The applicant must confirm and provide details, if applicable, regarding:
-
Any criminal cases pending against them in any jurisdiction.
-
Any penalties imposed for violation of securities or corporate laws.
-
Details of beneficial interest in any reporting body corporate, including the ultimate beneficiary.
-
Details of beneficial interest held in any body corporate.
-
Details of securities/contributions held.
-
Details of directorships or managerial positions held in any body corporate.
Attestation & Authentication of Documents
All KYC documents of the foreign national must be:
-
Notarized and Apostilled – if the country is a member of the Hague Apostille Convention.
-
Notarized and Consularized – if the country is not a member of the Hague Apostille Convention.
Alternatively, all documents may be Notarised and attested by the Indian Embassy in the applicant's country.
Details and Documents of the Existing Indian Company
To proceed with the appointment, the following information and documents of the Indian company are required:
-
Incorporation Documents – Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA).
-
Proposed date for holding the Board meeting.
-
Residential status of existing directors.
-
Name of authorised signatory for execution or issuance of certified true copies (CTC).
-
Proposed Certified True Copy of the Board Resolution for the appointment of a director from a land-border sharing country – we will provide the draft format (this is a mandatory prerequisite).
-
Complete address of the police station under whose jurisdiction the registered office is situated.
-
Latest utility bill (electricity/gas/telephone/mobile) – not older than 2 months.
-
Proof of registered office address – conveyance deed/lease deed/rent agreement along with rent receipts.
-
No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the owner if the registered office is not taken on lease.
-
Recent photograph of the registered office premises.
Therefore, the introduction of the DIN security clearance requirement by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs marks a decisive step in aligning corporate governance with national security considerations. While the Ease of Doing Business reforms have simplified company incorporation in India, the 2022 amendment to the Companies (Appointment and Qualification of Directors) Rules creates a clear distinction for nationals from countries sharing land borders with India, such as China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
For such individuals, obtaining prior clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is now a mandatory precondition before a Director Identification Number (DIN) can be allotted and at Compliance Calendar LLP, we understand the complexities that foreign investors and Indian companies face when navigating the DIN Security Clearance mandate and related regulatory processes. Our expertise lies in providing end-to-end support that ensures smooth compliance with both MCA and MHA requirements.











































































_crop10_thumb.jpg)


































































_crop10_thumb.jpg)
_crop10_thumb.jpg)



_crop10_thumb.jpg)


_crop10_thumb.jpg)





_crop10_thumb.jpg)

_crop10_thumb.jpg)














-suratgujarat-section-158_crop10_thumb.jpg)
-suratgujarat_crop10_thumb.jpg)
-(33)_crop10_thumb.jpg)



-ahmedabad_crop10_thumb.jpg)
-learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)

-learnn_crop10_thumb.jpg)



























































_crop10_thumb.jpg)























_Guidelines_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)























_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)
_crop10_thumb.jpeg)










_crop10_thumb.jpg)




_Second_Amendment_Rules,_2025_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)







_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)












































_learn_crop10_thumb.jpeg)




















_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)



_rd_roc_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)















_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)













_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)
_Learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)





































_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)




_learn_crop10_thumb.jpg)











_crop10_thumb.jpeg)